Structured Cabling
For domestic and commercial buildings alike, structured cabling for data and communications is every bit as important as the electricity. Whereas broadband was once an option it is now essential and this is as true of most homes as it is for businesses. As a contractor offering a full electrical and wiring service, structured cabling is now a substantial part of the Chancery Contracts business.
There are different types of cabling available and we supply and install each according to need. Which cabling is best is defined according to load/demand, the operating environment and, for businesses especially, how the demand and operating environment will change over time.
Most businesses want to grow and the installation should accommodate that. For new installations and re-fits alike, Chancery Contracts offers an initial, early stage, advisory service to ensure the right cabling is specified to cover existing and likely future requirements
The cabling we install falls into three broad categories, and details of each are outlined below.
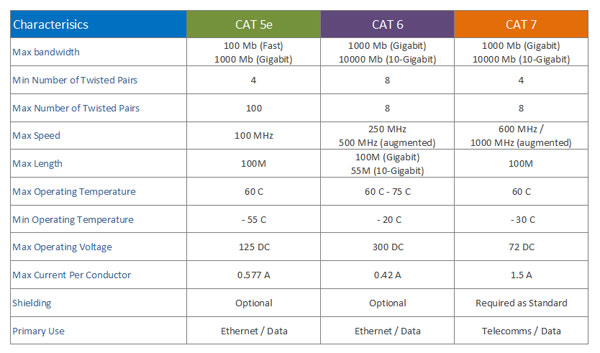
CAT 5e
 CAT 5 (Category 5) cabling has been around for some time now, CAT 5e is an enhanced version of the specification that continues to develop and now allows greater data volumes of up to 1 Gigabit (1 GB) and, in certain circumstances, up to 10 Gb.
CAT 5 (Category 5) cabling has been around for some time now, CAT 5e is an enhanced version of the specification that continues to develop and now allows greater data volumes of up to 1 Gigabit (1 GB) and, in certain circumstances, up to 10 Gb.
However, CAT 5 cabling is typically used for bandwidths of 10 Megabit (10Mb) to 100 Mb. Use of this cable for higher bandwidths is only viable on short cable runs. That is, as the data volume goes up, the length of cable between data management points goes down. For bandwidths up to 100Mb, 100m cable individual runs are possible.
This type of cabling constitutes the main ethernet data infrastructure for many small businesses especially. With the flexibility to carry both data and voice traffic it is highly flexible and covers a wide range of network requirements.
CAT 6
CAT 6 (Category 6) cabling is used mainly for ethernet / data installations and is aimed at higher data volumes (higher bandwidths), typically between 1Gb and 10Gb. It is made up of twisted pairs of cables which are arranged in such as way as inhibit data loss during transmission (packet loss). This allows for longer cable runs at high bandwidths, so that 100m runs are possible at 1Gb. However, the augmented version of this type of cable (CAT6a) can run at higher frequencies and can deal with 100m cable runs at bandwidths of up to 10Gb.
Although (as you might expect) the cost per metre of CAT6/CAT6a cabling is more than CAT5, this can prove to be an investment as data demand continues to grow exponentially, even if the business does not.
CAT 7
CAT (category 7), or Class F cabling is a heavier duty cable that is shielded for added data loss protection. As with the cables above, it is also comprised of multiple twisted pair cables, but has more flexibility for carrying higher loads and combinations of voice and data. It is mainly used for telecomms applications, but data networks can run off the same installation if needs be.
The table below gives a breakdown of the some of the main characteristics of each cable type.
Chancery Contracts works with both commercial and domestic clients on new builds, or on re-fits. If you would like to know more about our structured cabling advisory an installation services please get in touch.